

If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) has overlapping polygons, the zonal analysis will not be performed for each individual polygon.
For such cells, the zone value is determined by the point with the lowest ObjectID field (for example, OID or FID). If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) is a point feature, it is possible to have more than one point contained within any particular cell of the value input raster.
.jpg)
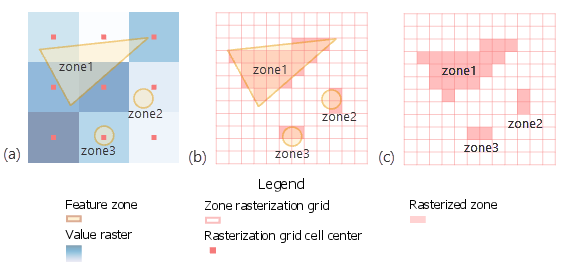
You can manage this by determining an appropriate value for the Cell Size environment that will preserve the desired level of detail of the feature zones, and specify it in the analysis environment. As a result, those zones will not be represented in the output. If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) is a feature, for any of the zone features that do not overlap any cell centers of the value raster, those zones will not get converted to the internal zone raster. If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) is a feature, it will be converted to a raster internally, using the cell size and cell alignment from the Input value raster ( in_value_raster in Python). If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) is a raster, it must be an integer raster. When the zone and value inputs are both rasters of the same cell size and the cells are aligned, they will be used directly in the tool, and will not be resampled internally during the tool execution. Either of these cases will trigger an internal resampling before the zonal operation is performed. If the cell size is same, but the cells are not aligned, the Input value raster will be used as the snap raster internally. When the Cell size of the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) and the Input value raster ( in_value_raster in Python) is different, the output cell size will be the Maximum Of Inputs, and the Input value raster will be used as the Snap Raster internally. Both raster and feature can be used for the zone input. Learn more about how Zonal Statistics works Illustration OutRas = ZonalStatistics(ZoneRas, "VALUE", ValRas, "MINIMUM") UsageĪ zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. Calculates statistics on values of a raster within the zones of another dataset.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
